Dalam blog post ini, akan mempelajari langkah-langkah untuk mengaktifkan otentikasi dua faktor (2FA) menggunakan Google Authenticator di Ubuntu, menambah lapisan keamanan pada akun Linux Ubuntu.
Pertama, pasang paket google-authenticator di Ubuntu dengan menjalankan perintah sudo apt-get install libpam-google-authenticator.
sudo apt install libpam-google-authenticator
Contoh outputnya :
root@svr-workshop:~# apt install libpam-google-authenticator Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: linux-headers-5.15.0-78 linux-headers-5.15.0-78-generic linux-image-5.15.0-78-generic linux-modules-5.15.0-78-generic linux-modules-extra-5.15.0-78-generic Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following additional packages will be installed: libqrencode4 The following NEW packages will be installed: libpam-google-authenticator libqrencode4 0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 66 not upgraded. Need to get 69.7 kB of archives. After this operation, 205 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://id.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libqrencode4 amd64 4.1.1-1 [24.0 kB] Get:2 http://id.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libpam-google-authenticator amd64 20191231-2 [45.7 kB] Fetched 69.7 kB in 8s (9109 B/s) debconf: delaying package configuration, since apt-utils is not installed Selecting previously unselected package libqrencode4:amd64. (Reading database ... 134843 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libqrencode4_4.1.1-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libqrencode4:amd64 (4.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpam-google-authenticator. Preparing to unpack .../libpam-google-authenticator_20191231-2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpam-google-authenticator (20191231-2) ... Setting up libqrencode4:amd64 (4.1.1-1) ... Setting up libpam-google-authenticator (20191231-2) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.8) ... debconf: unable to initialize frontend: Dialog debconf: (No usable dialog-like program is installed, so the dialog based frontend cannot be used. at /usr/share/perl5/Debconf/FrontEnd/Dialog.pm line 78.) debconf: falling back to frontend: Readline Scanning processes... Scanning candidates... Scanning linux images... Pending kernel upgrade ---------------------- Newer kernel available The currently running kernel version is 5.15.0-97-generic which is not the expected kernel version 5.15.0-117-generic. Restarting the system to load the new kernel will not be handled automatically, so you should consider rebooting. Restarting services... Daemons using outdated libraries -------------------------------- 1. networkd-dispatcher.service 4. ssh.service 7. systemd-manager 10. systemd-timesyncd.service 13. [email protected] 2. packagekit.service 5. systemd-journald.service 8. systemd-networkd.service 11. systemd-udevd.service 14. [email protected] 3. polkit.service 6. systemd-logind.service 9. systemd-resolved.service 12. unattended-upgrades.service 15. none of the above (Enter the items or ranges you want to select, separated by spaces.) Which services should be restarted? Service restarts being deferred: systemctl restart networkd-dispatcher.service systemctl restart packagekit.service systemctl restart polkit.service systemctl restart ssh.service systemctl restart systemd-journald.service systemctl restart systemd-logind.service /etc/needrestart/restart.d/systemd-manager systemctl restart systemd-networkd.service systemctl restart systemd-resolved.service systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd.service systemctl restart systemd-udevd.service systemctl restart unattended-upgrades.service systemctl restart [email protected] systemctl restart [email protected] No containers need to be restarted. No user sessions are running outdated binaries. No VM guests are running outdated hypervisor (qemu) binaries on this host. root@svr-workshop:~#
Untuk memulai konfigurasi 2FA
tambahkan auth required pam_google_authenticator.so pada konfigurasi /etc/pam.d/common-auth (baris kode ke 18)
root@svr-workshop:~# nano /etc/pam.d/common-auth
Berikut ini contoh file konfigurasi setelah di tambahkan
root@svr-workshop:~# cat /etc/pam.d/common-auth # # /etc/pam.d/common-auth - authentication settings common to all services # # This file is included from other service-specific PAM config files, # and should contain a list of the authentication modules that define # the central authentication scheme for use on the system # (e.g., /etc/shadow, LDAP, Kerberos, etc.). The default is to use the # traditional Unix authentication mechanisms. # # As of pam 1.0.1-6, this file is managed by pam-auth-update by default. # To take advantage of this, it is recommended that you configure any # local modules either before or after the default block, and use # pam-auth-update to manage selection of other modules. See # pam-auth-update(8) for details. ## Tambahkan google authenticator disini auth required pam_google_authenticator.so # here are the per-package modules (the "Primary" block) auth [success=1 default=ignore] pam_unix.so nullok # here's the fallback if no module succeeds auth requisite pam_deny.so # prime the stack with a positive return value if there isn't one already; # this avoids us returning an error just because nothing sets a success code # since the modules above will each just jump around auth required pam_permit.so # and here are more per-package modules (the "Additional" block) auth optional pam_cap.so # end of pam-auth-update config root@svr-workshop:~#
Edit file konfigurasi PAM (/etc/pam.d/sshd) untuk menambahkan baris auth required pam_google_authenticator.so. Ini memastikan bahwa setiap login SSH memerlukan kode dari Google Authenticator. (baris kode ke 8)
root@svr-workshop:~# nano /etc/pam.d/sshd
Berikut ini contoh file konfigurasi setelah di tambahkan
root@svr-workshop:~# cat /etc/pam.d/sshd # PAM configuration for the Secure Shell service # Standard Un*x authentication. @include common-auth # two-factor authentication via Google Authenticator auth required pam_google_authenticator.so # Disallow non-root logins when /etc/nologin exists. account required pam_nologin.so # Uncomment and edit /etc/security/access.conf if you need to set complex # access limits that are hard to express in sshd_config. # account required pam_access.so # Standard Un*x authorization. @include common-account # SELinux needs to be the first session rule. This ensures that any # lingering context has been cleared. Without this it is possible that a # module could execute code in the wrong domain. session [success=ok ignore=ignore module_unknown=ignore default=bad] pam_selinux.so close # Set the loginuid process attribute. session required pam_loginuid.so # Create a new session keyring. session optional pam_keyinit.so force revoke # Standard Un*x session setup and teardown. @include common-session # Print the message of the day upon successful login. # This includes a dynamically generated part from /run/motd.dynamic # and a static (admin-editable) part from /etc/motd. session optional pam_motd.so motd=/run/motd.dynamic session optional pam_motd.so noupdate # Print the status of the user's mailbox upon successful login. session optional pam_mail.so standard noenv # [1] # Set up user limits from /etc/security/limits.conf. session required pam_limits.so # Read environment variables from /etc/environment and # /etc/security/pam_env.conf. session required pam_env.so # [1] # In Debian 4.0 (etch), locale-related environment variables were moved to # /etc/default/locale, so read that as well. session required pam_env.so user_readenv=1 envfile=/etc/default/locale # SELinux needs to intervene at login time to ensure that the process starts # in the proper default security context. Only sessions which are intended # to run in the user's context should be run after this. session [success=ok ignore=ignore module_unknown=ignore default=bad] pam_selinux.so open # Standard Un*x password updating. @include common-password root@svr-workshop:~#
Membuat file configurasi untuk google authenticator
root@svr-workshop:~# nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/00-google-authenticator.conf
Isi filenya sebagai berikut :
# special settings for using the Google Authenticator # IMPORTANT: For this to work # * The PAM module must have been installed # * and added to /etc/pam.d/sshd # These options must excplicitly be set, even though they might be the default. # sshd uses the first entry it finds and ignores any subsequent entries. # So if any other config file in /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d sets this later on # this entry will still be used. # KbdInteractiveAuthentication # Specifies whether to allow keyboard-interactive authentication. # The default is yes. # The argument to this keyword must be yes or no. # ChallengeResponseAuthentication is a deprecated alias for this. KbdInteractiveAuthentication yes # PasswordAuthentication # Specifies whether password authentication is allowed. The default is yes. PasswordAuthentication yes
Berganti user ke user yang akan di berikan 2FA
Jalankan perintah google-authenticator untuk menghasilkan kode QR dan kunci pemulihan. Ikuti petunjuk untuk menyiapkan autentikasi dua faktor dan simpan informasi pemulihan dengan aman.
root@svr-workshop:~# su - labsuser labsuser@svr-workshop:~$ labsuser@svr-workshop:~$ google-authenticator -t Warning: pasting the following URL into your browser exposes the OTP secret to Google: https://www.google.com/chart?chs=200x200&chld=M|0&cht=qr&chl=otpauth://totp/labsuser@svr-workshop%3Fsecret%3DUMJZHP5FAFC3OCHPX3IZWAO4NA%26issuer%3Dsvr-workshop .. ..
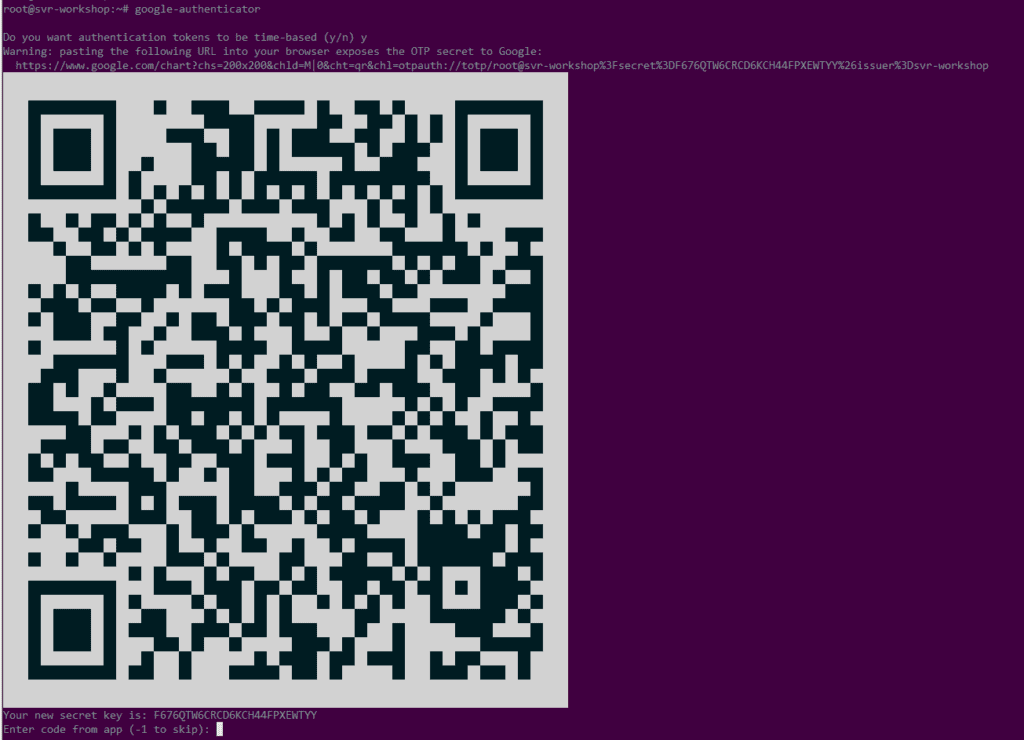

Your new secret key is: F676QTW6CRCD6KCH44FPXEWTYY Enter code from app (-1 to skip): 331617 Code confirmed Your emergency scratch codes are: 27821167 17396699 26602198 60731254 17282647 Do you want me to update your "/home/labsuser/.google_authenticator" file? (y/n) y Do you want to disallow multiple uses of the same authentication token? This restricts you to one login about every 30s, but it increases your chances to notice or even prevent man-in-the-middle attacks (y/n) y By default, a new token is generated every 30 seconds by the mobile app. In order to compensate for possible time-skew between the client and the server, we allow an extra token before and after the current time. This allows for a time skew of up to 30 seconds between authentication server and client. If you experience problems with poor time synchronization, you can increase the window from its default size of 3 permitted codes (one previous code, the current code, the next code) to 17 permitted codes (the 8 previous codes, the current code, and the 8 next codes). This will permit for a time skew of up to 4 minutes between client and server. Do you want to do so? (y/n) n If the computer that you are logging into isn't hardened against brute-force login attempts, you can enable rate-limiting for the authentication module. By default, this limits attackers to no more than 3 login attempts every 30s. Do you want to enable rate-limiting? (y/n) y labsuser@svr-workshop:~#
Coba lakukan sudo su dengan user tersebut
labsuser@svr-workshop:~$ sudo su Verification code: [sudo] password for labsuser: root@svr-workshop:/home/labsuser# root@svr-workshop:/home/labsuser#
Akan muncul permintaan kode otp sebelum memasukkan password
Coba melakukan login melalui ssh juga akan muncul permintaan kode verifikasi (otp)
C:\Users\thinksystem>ssh [email protected] ([email protected]) Verification code: ([email protected]) Password: ([email protected]) Verification code: Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.0-97-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage This system has been minimized by removing packages and content that are not required on a system that users do not log into. To restore this content, you can run the 'unminimize' command. Last login: Sun Aug 4 08:48:35 2024 from 192.168.1.191 labsuser@svr-workshop:~$